- Home
-
Discover
-
Engage
- MTSummit2024
-
About
- Login




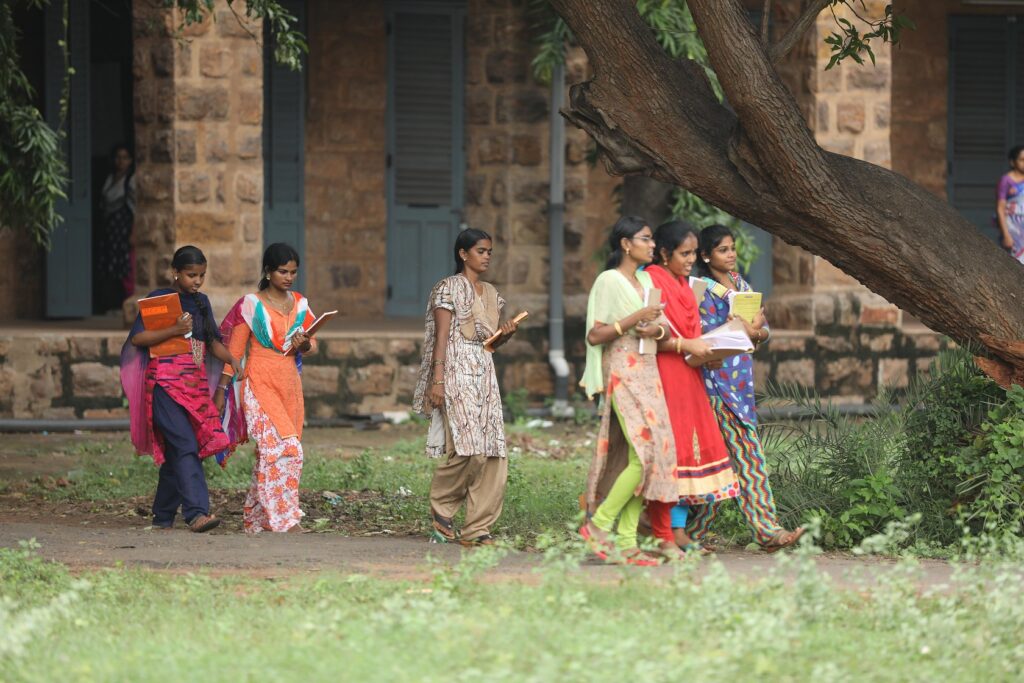






Mentor Together empowers young people from underprivileged backgrounds by providing them with one-on-one mentoring relationships. These invaluable relationships foster personal growth, boost confidence, and equip mentees with the necessary skills to overcome challenges and achieve their aspirations.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Sign up for our
Newsletter